How to Optimize Your Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments are the invisible engine behind your international checkout button.
Behind every sale that crosses a border are a bunch of processes invisible to the seller and shopper, including currency conversions, regulatory issues, and bank approvals.
As global commerce intensifies, the market for these transactions is scaling fast. The global cross-border payments market is estimated to be worth $198.6 billion in 2024. It’s expected to more than double by 2034, reaching approximately $413.1 billion, driven by a consistent compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6%.

Let’s peel back the layers of cross-border payments and break down the essential elements that make international transactions work smoothly.
What are Cross-Border Payments?
Cross border payments are financial transactions that occur between parties based in separate countries, meaning the sender and recipient operate under different national financial systems. Here are a few examples:
- A customer in Germany buying a smartwatch from Amazon Japan; the transaction involves currency conversion from euros to yen.
- A freelance graphic designer in the Philippines getting paid in USD by a client in Canada via PayPal or Wise.
- A U.S.-based ecommerce brand sourcing eco-friendly packaging from a supplier in Vietnam, paying through a B2B cross-border bank transfer.
So, what is a cross border transaction? In simple terms, it’s a payment that crosses national boundaries, triggering a chain of processes that often involve:
- Currency conversion
- Regulatory checks
- Settlement through various banks and payment networks
For Amazon international sellers, cross-border payments are a core part of operations. Sellers need to receive funds in their local bank accounts, even when their customers shop from different parts of the world.
This is where challenges like a heavy cross-border payment fee come into play. These charges—often labeled as a cross-border fee—are applied by banks, card networks, or payment processors for handling transactions across jurisdictions.
It goes without saying that cross-border transactions are crucial in today’s global marketplace. In fact, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) and the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI) proposed a global roadmap to improve these payments.
Initiated in 2020 and designed as a multi-year initiative running through 2027, the FSB and CPMI’s cross-border payments roadmap is guided by five key focus areas:
- Public and Private Sector Commitment
- Regulatory, Supervisory, and Oversight Frameworks
- Existing Payment Infrastructures
- Data and Market Practices
- New Infrastructures and Arrangements

The roadmap aims to resolve cross-border payments issues, including high costs, slow delivery, unpredictable fees, and limited transparency.
Cross-Border Payments vs Domestic Payments
Cross-border payments differ from domestic payments in several key ways, primarily due to the added layers of complexity involved when money moves between countries.
While domestic transactions typically occur within the same banking system, currency, and regulatory environment, cross-border payments must navigate the following factors:
- Multiple financial institutions
- Different currencies
- Time zones
- Jurisdiction-specific compliance requirements
These transactions often involve currency conversion, incur foreign exchange fees, and take longer to settle due to intermediary banks and anti-fraud checks.
Additionally, cross-border payments are more prone to failures or delays, making optimization essential for businesses engaged in international payments.
Key Components of Cross-Border Transactions
Here are the core components that power seamless cross-border payments for today’s businesses and consumers:
Payment Gateways and Global Processing Infrastructure
A payment gateway acts as the bridge between the customer’s payment method and the merchant’s bank.
For ecommerce payments especially, choosing the right gateway can make or break your cross-border strategy. To reduce the friction of selling abroad, leading global payment processing providers offer features like:
- Fraud protection
- Currency handling
- Multi-country settlement
Payment Localization
To boost conversions, businesses must tailor the checkout experience to each market. Payment localization involves:
- Displaying prices in local currencies
- Offering region-preferred payment methods
- Using native language interfaces
Currency Conversion and Foreign Exchange Fees
When a buyer pays in a different currency than the seller’s, the amount must be converted. This is where foreign exchange fees come into play, typically charged by banks, card networks, or payment gateways. The amount charged can fluctuate based on multiple factors, such as:
- The region
- Payment method
- Service provider
For ecommerce businesses, minimizing these fees can make a big difference in overall profitability. After all, consumers are fee-conscious. Mastercard’s Borderless Payments Report 2023 reveals that 43% of global users say that lower fees for sending and receiving money are the most important factor when choosing a brand or platform for cross-border payments.

Compliance, Risk, and Settlement Processes
Cross-border transactions must adhere to a host of regional regulations. These regulations include the following standards:
- Anti-money laundering (AML)
- Know your customer (KYC)
- Data protection practices
Providers of cross border payment solutions often handle much of this compliance work.
Market Expansion Tools
Companies going global rely on tech platforms that support market expansion through features like:
- Multicurrency pricing
- Tax calculation engines
- Integrated logistics
The more efficient your international payment setup, the smoother your customer experience.
Top Platforms for Managing Cross-Border Payments
Here are some of the most popular cross-border payments platforms used by ecommerce ventures around the globe:
Stripe
Stripe is a go-to solution for global ecommerce brands, offering seamless international payments, multicurrency support, and payment localization tools. With Stripe Checkout and Connect, sellers can reach buyers in over 135 countries.
- Best for. Startups and online brands needing developer-friendly customization.
PayPal
PayPal is one of the most trusted platforms for cross-border payments, particularly among small businesses. It supports transactions in over 100 currencies and is widely used by international customers around the world. Sellers can also access working capital and dispute resolution features.
- Best for. Ecommerce stores targeting a broad, international customer base.
Wise
Wise offers transparent currency conversion and real-time exchange rates, helping sellers lower their cross-border payment fees. It’s popular for B2C and freelancer payouts, with a multi-currency business account for global operations.
- Best for. Small businesses looking to reduce hidden FX charges
BlueSnap
BlueSnap is built for global payment processing, offering features like smart routing, fraud prevention, and support for over 100 payment types. It also allows for embedded payments via API and checkout customization.
- Best for. Mid-sized businesses and growing ecommerce brands
Payoneer
Favored by Amazon international sellers and global freelancers, Payoneer enables cross-border fund transfers, virtual accounts in multiple currencies, and direct withdrawals to local banks.
- Best for. Marketplace sellers, remote teams, and suppliers needing flexible withdrawal options
The FXC Intelligence reported over 30 companies projected to earn $1 billion or more in cross-border payments revenue in 2024, including ecommerce-friendly platforms like Payoneer and Wise.
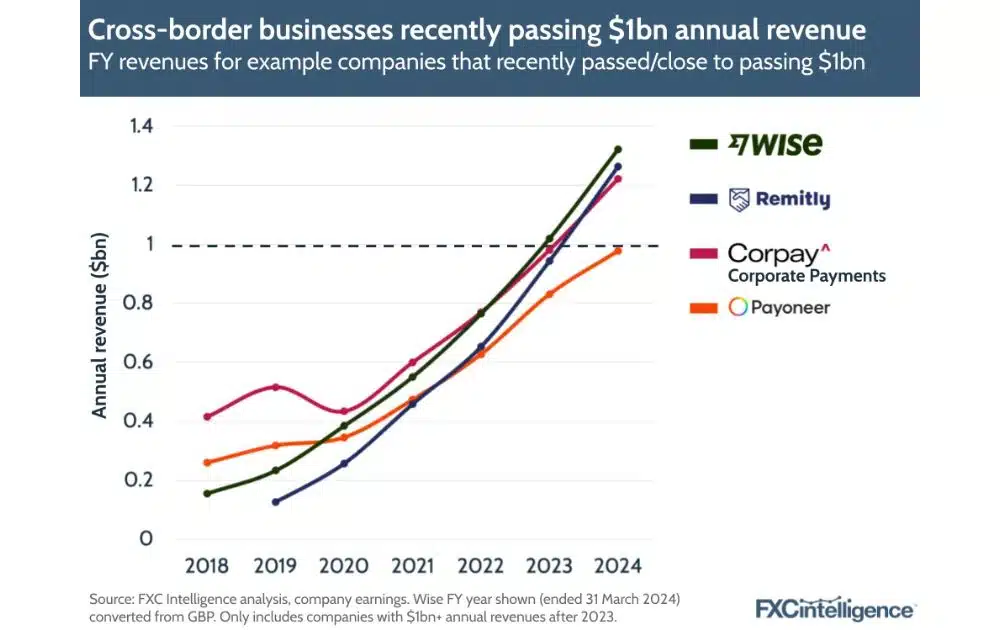
Meanwhile, Remitly and Corpay, typically used for remittances and B2B treasury and payroll solutions, respectively, were also among the fastest-growing companies within cross-border payment solutions.
Strategies to Optimize Your Cross-Border Payments
Here are key strategies that tackle compliance, tax and other financial implications of selling internationally, especially for cross-border ecommerce brands and Amazon Global Selling participants:
Streamline Tax Registration and VAT Compliance
Selling internationally means navigating a web of tax obligations, from VAT number in the EU to GST (Goods and Services Tax) in Australia.
If you’re part of Amazon Global Selling, some regions require a valid VAT number―like the UK―to list products or avoid account suspension. Not registering properly can lead to unexpected fees, fines, or blocked payouts.
Proactively research your tax obligations in each target country. Use Amazon’s VAT Services (or a third-party tax platform) to automate filings and stay compliant.
- Actionable Tip. If you’re unsure where to start, consult AMZ Advisers to get expert guidance on your ecommerce business, including VAT registration to help reduce selling fees related to non-compliance.
Factor in Global Selling Fees and Currency Exchange Costs
Amazon applies various fees to international sellers, including Amazon Global Selling referral fees, fulfillment costs, and exchange rate fees when converting earnings. Many sellers overlook these in their pricing strategy.
Use Amazon’s FBA revenue calculator to estimate total costs across regions. Build these fees and potential cross-border payments charges into your pricing models to protect margins.
- Actionable Tip. Consider using Amazon’s local bank disbursement option (where available) to avoid unfavorable FX conversions and third-party banking fees.
Stay Ahead of Compliance and Regulatory Shifts
Cross-border transactions must comply with local financial laws, especially around anti-money laundering, know your customer rules, and transaction limits. Not complying properly can lead to frozen funds, chargebacks, or even blacklisting.
Work with a payment service provider or gateway that monitors regulatory updates and automates these processes during customer onboarding.
- Actionable Tip. Audit your payment flows annually and ensure your service provider complies with the latest regulations in every region you sell to.
Final Thoughts
Cross-border payments may happen in the background, but they carry front-line consequences for ecommerce businesses aiming to scale globally.
Whether you’re selling on Amazon or managing your own ecommerce website, success comes down to choosing the right partners, staying ahead of regulations, and building financial strategies that protect your bottom line.
Author
 Carla Bauto Deña is a journalist and content writer producing stories for traditional and digital media. She believes in empowering small businesses with the help of innovative solutions, such as ecommerce, digital marketing, and data analytics.
Carla Bauto Deña is a journalist and content writer producing stories for traditional and digital media. She believes in empowering small businesses with the help of innovative solutions, such as ecommerce, digital marketing, and data analytics.
The post How to Optimize Your Cross-Border Payments appeared first on AMZ Advisers.


